What Is The Difference Between A Handheld And Benchtop Multimeter?
The main difference between a handheld and benchtop multimeter is portability and precision. Handheld multimeters are compact and designed for field use, making them ideal for quick, basic measurements on job sites or factory floors. Benchtop multimeters are larger and are built for laboratory or engineering environments that offer significantly higher accuracy, advanced features, and capabilities for precise applications.
Outside of making the decision to choose an analog or digital multimeter, the next most important decision is to choose between benchtop and handheld multimeters.
There is no doubt that handheld multimeters are far more common than benchtop multimeters. Given that the multimeter is something of the general workhorse of all electrical measurements, it makes sense that the more portable option would be more popular.
However, there are plenty of scenarios where you will need a far more specialized piece of equipment – for example when extremely accurate measurements are necessary. That is where the benchtop multimeter comes into play.
This article delves into the comparison between benchtop and handheld multimeters, outlining their features, benefits, and applications to help you make an informed decision.
In This Article:
This is the seventh article in our series, The Definitive Guide to Multimeters.
If you missed the last part of the series: Analog vs. Digital Multimeters, check it out now! You will be able to work your way back to this article quite quickly.
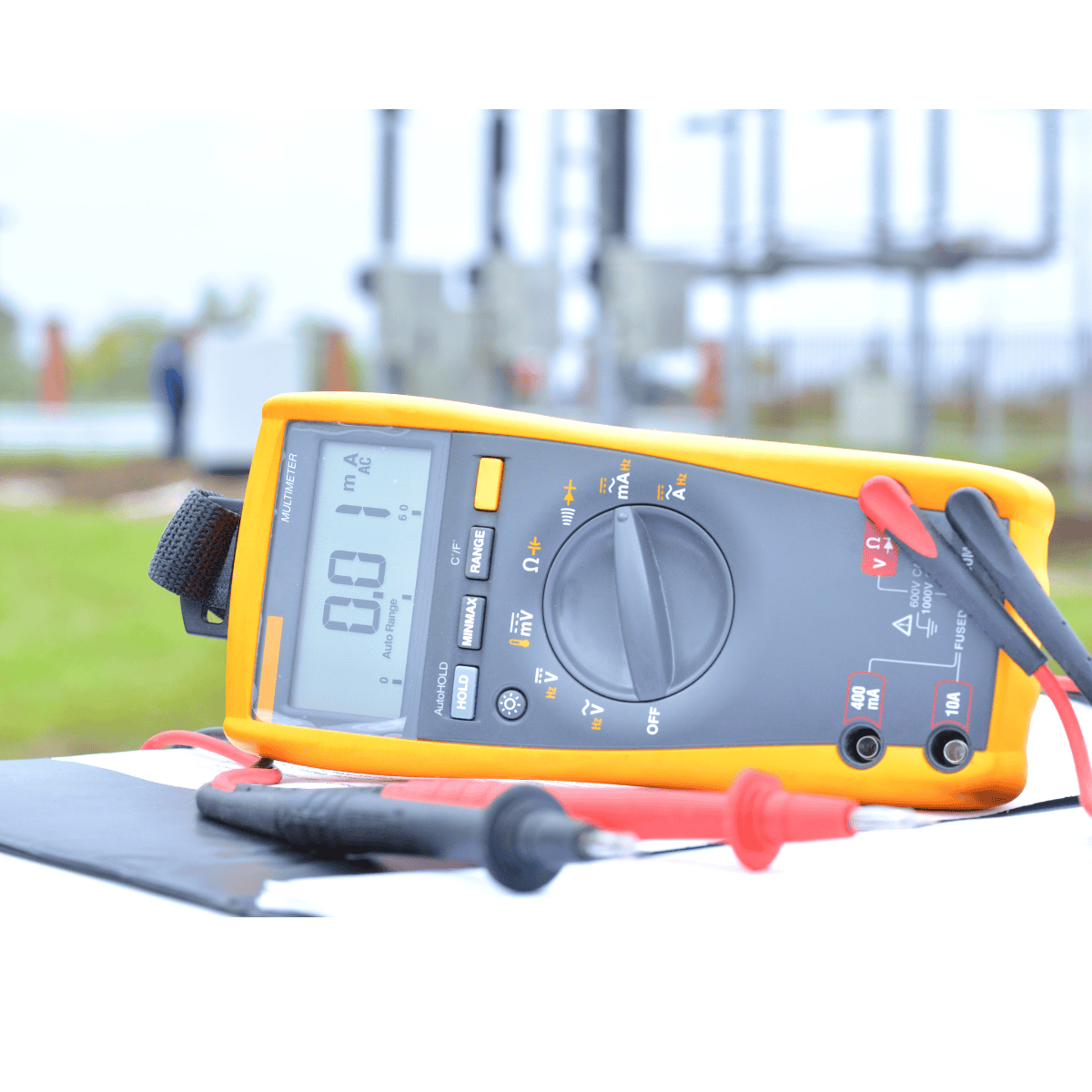
What Are Handheld Multimeters?
Handheld multimeters are portable electric measurement devices designed to be held and operated with a single hand. They are compact, lightweight, and battery-powered, making them highly convenient for on-the-go measurements. Despite their smaller size, handheld multimeters offer a wide range of features and capabilities.
Most electrical measurement applications are going be done in the “field”, whether that be at a job site or on a machine on a factory floor. As a result, the handheld multimeter is a far more common instrument.
Handheld multimeters are intended for use in the field. Their primary focus is on portability, so the user can quickly and easily make basic voltage, current and resistance measurements on the fly.
Simply put, the types of measurements done in the field are commonly not complex. As a result, things like accuracy and advanced features are commonly less important.

Advantages of Handheld Multimeters
There are several relative advantages to selecting a handheld multimeter over a benchtop multimeter:
- Portability
- Cost
- Size
Portability
Handheld multimeters are more portable for on-site measurements.
Cost
Most handheld multimeters have a lower cost compared to benchtop models.
Size
Typically, handheld multimeters are the ideal for basic electronic tasks.
Things To Consider Before Buying A Handheld Multimeter
Before opting to buy a handheld multimeter, it is essential to consider the following factors:
- Accuracy and Precision
- Display Size
- Safety Features
Accuracy And Precision
Handheld multimeters generally provide sufficient accuracy for most applications. However, if high-precision measurements are crucial for your work, a benchtop multimeter may be a better choice.
Display Size
Due to their compact nature, handheld multimeters typically have smaller displays compared to benchtop models. Ensure the display is large enough for comfortable reading, especially in dimly lit environments.
Safety Features
Depending on your specific requirements, check if the handheld multimeter offers features like overload protection, fused current inputs, and CAT safety ratings to ensure safe measurements in hazardous conditions.
What Are Benchtop Multimeters?
Benchtop multimeters, also known as desktop or laboratory multimeters, are larger, stationary devices designed for more demanding applications. They offer enhanced precision, accuracy, and a broader range of measurement options compared to their handheld counterparts. Benchtop multimeters are typically powered through an AC power source, providing stable and reliable performance.
In more advanced fields, it is often that the need for high levels of accuracy comes up – especially when working with extremely low currents and voltages.
This is an environment where benchtop multimeters are very common. Some benchtop multimeters can even measure out to 8.5 digits, compared to 3.5 or 4.5 digits for handheld multimeters.
Most benchtop multimeters are quite larger than handheld multimeters. Typically they spend their lives stationed on an engineer’s desk or mounted in a testing rack. Oftentimes a benchtop multimeter will be used in settings where automated testing is required.

Advantages of Benchtop Multimeters
There are several relative advantages to selecting a benchtop multimeter over its handheld counterpart:
- Accuracy
- Enhanced Features
- Automation
- Display Size
Accuracy
Benchtop multimeters have higher accuracy in measurements. It is not unheard of to have benchtop multimeters that can measure out 8.5 digits. With this level of precision and accuracy, routine traceability and calibration become especially important to ensure the measurements remain reliable in high quality environments.
Enhanced Features
Greater functionality and measurement options. There is almost no limit to what a benchtop multimeter can measure. Additionally, you will get far more data recording options.
Automation
Benchtop multimeters offer the capability to automate the measurement process for all standard units via remote control and data recording.
Display Size
Most multimeters typically have much larger displays for easy reading, in addition to the data output options that exist.
Things To Consider Before Buying A Benchtop Multimeter
Before investing in a benchtop multimeter, consider the following aspects:
- Cost
- Space and Portability
- Learning Curve
Cost
Benchtop multimeters tend to be more expensive compared to handheld models, especially when higher accuracy and additional features are required. Assess your budget and requirements accordingly.
Space and Portability
Benchtop multimeters require a dedicated workspace and power source. If portability is a priority or space is limited, a handheld multimeter might be a more practical choice.
Learning Curve
Benchtop multimeters often have more complex interfaces and advanced features, which may require a learning curve to fully utilize their capabilities. Ensure you have the necessary expertise or training to make the most of the instrument.
Conclusion
Both handheld and benchtop multimeters serve essential roles in electrical measurement where both excel in different environments. Handheld models offer unmatched portability and convenience for quick field testing, while benchtop multimeters deliver superior accuracy and advanced functionality for laboratory or engineering applications. Understanding the strengths of each helps ensure you select the right tool for your specific needs.
Handheld Vs. Benchtop Mulitmeter FAQs
Q1. Are handheld multimeters accurate enough for professional use?
Yes, with ±0.5% accuracy, handheld multimeters suit most professional field tasks like EV or solar testing.
Q2. Why are benchtop multimeters more accurate?
Benchtop multimeters are more accurate due to their stable power and advanced circuitry allow up to 8.5-digit precision.
Q3. Can handheld digital multimeters handle smart features?
Yes, many handheld digital multimeters offer IoT connectivity and cloud data logging.
Q4. Are benchtop multimeters worth the cost?
If you are working in a lab or do automated testing, then yes, benchtop multimeters are worth the cost due to their precision and automation capabilities.
The Definitive Guide To Multimeters
What’s Next: What Is A True-RMS Multimeter?
As far as multimeter construction goes, we have now covered the two most common distinctions: analog vs. digital display and handheld vs. benchtop multimeters.
In the next section, we will dive into one of the most prevalent types of multimeters, True-RMS multimeters, how they operate and why they are important. Let’s get started and head to Section 8: True-RMS Multimeters.
ISO/IEC 17025 Accredited Multimeter Calibration
Fox Valley Metrology offers precise multimeter calibration for any make or model. Our ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation guarantees testing to the highest industry standards. We offer fast, reliable in-lab or onsite calibration services to fit your needs and schedule.
- ✓ ISO/IEC 17025 accredited calibration vendor
- ✓ Broadest calibration scope in the industry
- ✓ 3-5 day turnaround time in-lab calibrations
- ✓ Pickup and delivery service options
- ✓ Onsite calibration available