Should I Use An Analog Or Digital Multimeter?
In most cases a digital multimeter will be your best choice to use as it provides higher accuracy, clear numerical readings, and modern features like auto-ranging and added safety protections. However, an analog multimeter can be better the better choice for viewing fluctuating signals and doesn’t rely on battery power.
With most new multimeters being manufactured with a digital display, it may be tempting to assume that it is a slam-dunk decision to opt for a digital multimeter over an analog multimeter. After all, the world is moving to a more and more digitized.
In most cases, that would be correct. However, there are some important advantages and disadvantages to take into account when deciding which to use.
This article discusses the pros and cons of analog vs. digital multimeters.
In This Article:
- The Pros Of Using a Digital Multimeter
- The Cons Of Using a Digital Multimeter
- The Pros Of Using an Analog Multimeter
- The Cons Of Using an Analog Multimeter
- Digital Vs. Analog Multimeters FAQs
This is the sixth article in our series, The Definitive Guide to Multimeters.
If you missed the last part of the series: Digital Multimeters: How They Work and Their Role Today, check it out now! You will be able to work your way back to this article quite quickly.
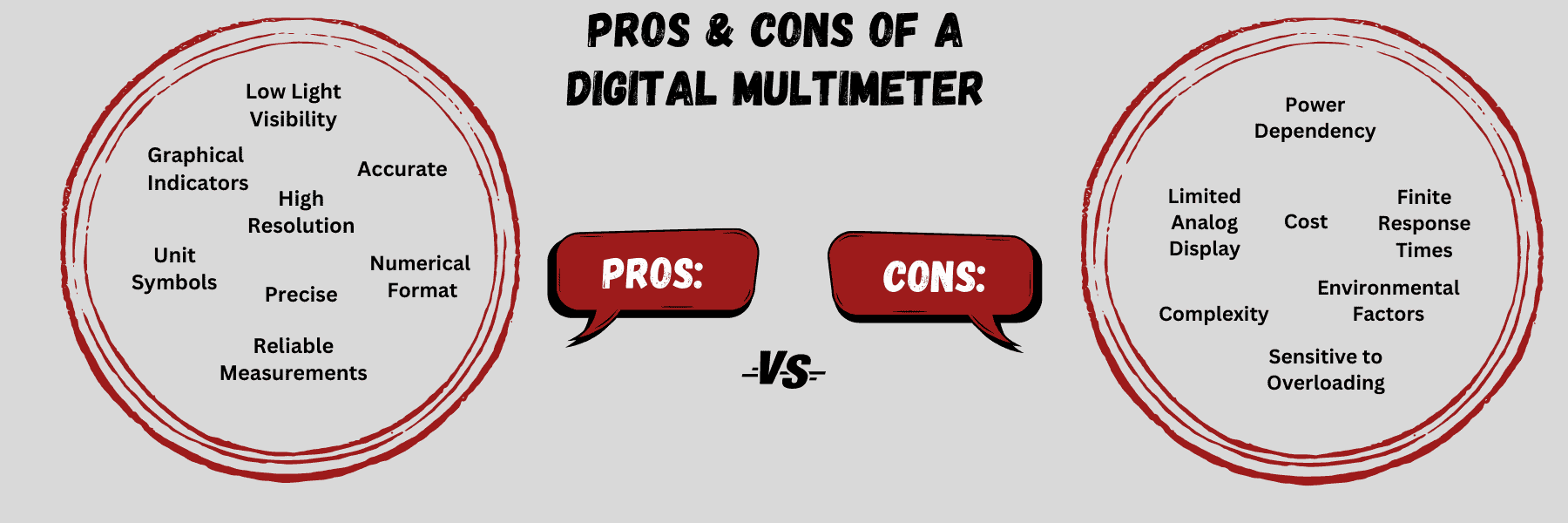
The Pros Of Using A Digital Multimeter
A digital multimeter is certainly the most common multimeter these days. There are a lot of good reasons why, such as:
- Accuracy & Precision
- Numerical Display
- Automatic Measurement Recording
- Additional Display features
- Higher Impedance
- Low Light Visibility
- Increased Durability
- Additional Safety Features
- Faster Measurements
Accuracy & Precision
Provides precise and accurate readings (typically ranging from ±0.1% to ±1%), often with high-resolution decimal places, ensuring clear and reliable measurements. Regardless of whether you choose an analog or digital multimeter, maintaining that level of performance requires calibration to ensure the readings remain accurate.
Numerical Display
The numerical format eliminates the potential for parallax errors associated with analog scales, enhancing the accuracy of the displayed values.
Automatic Measurement Recording
Recording of measurements on digital multimeters is often automatic, meaning you will not need to stop frequently to write down the measurements you are taking.
Additional Display Features
Digital displays also allow for additional features such as automatic decimal point placement, unit symbols, and graphical indicators.
Higher Impedance
Digital multimeters have higher impedance, meaning less impact on the circuit you are measuring.
Low Light Visibility
Some digital multimeters may incorporate additional display features such as backlighting for improved visibility in low-light conditions or bar graphs to provide visual representations of signal levels or trends.
Increased Durability
Digital multimeters can be less susceptible to wear and aging of their internal components, which may affect accuracy over time.
Additional Safety Features
They often have auto-polarity features, which helps prevent against you selecting the wrong polarity when measuring. Also, many contain auto-ranging features also. This will help protect your multimeter in the event you accidentally select the wrong range.
The Cons Of Using A Digital Multimeter
While the digital multimeter certainly offers a lot of relative advantages over an analog multimeter, its not all sunshine and roses. Some of the more obvious disadvantages of using a digital multimeter are:
- Finite response Time
- Interference Susceptibility
- Power Dependency
- Complexity
- Cost
- Overheating Risk
Finite Response Time
Digital multimeters have a finite response time, which is the time it takes for the multimeter to update and display a new measurement value. In applications where rapid changes or transient signals need to be measured, the response time of a digital multimeter may limit its usefulness.
Interference Susceptibility
Digital multimeters, particularly those with sensitive measurement functions like low-level voltage or current measurements, can be susceptible to interference from external electromagnetic fields or noise. Proper shielding and grounding techniques should be employed to minimize the influence of such factors and ensure accurate readings.
Power Dependency
The digital display can often wear out battery life much faster than you would like. This is especially an issue on units where the display dims as the battery drains. If you are working outside while the display dims, it can become very difficult to read.
Complexity
The digital multimeter is simply more complex than an analog multimeter. The initial learning curve is greater as a result. This is especially of concern if numerous people are going to be using the multimeter.
Cost
Simply put, digital multimeters are typically the more expensive option compared to analog multimeters.
Overheating Risk
Sometimes, the internal components of the digital multimeter can cause it to overheat. They are more complex than that of an analog multimeter. This extra complexity can cause issues.
The Pros Of Using An Analog Multimeter
While it may seem like the analog multimeter is an antiquated device with not much purpose in an increasingly digital world, there are still some applications where an analog multimeter has stronger benefits:
- Can Measure Fluctuating Signals
- Can Measure Minimum and Maximum Values Quicker
- No Dependency on Power
- Lower Cost
- Lower Complexity
Can Measure Fluctuating Signals
If the signal you are measuring is fluctuating, most digital multimeters often give you an average, not a true range of that signal. Analog multimeters will allow you to see the full range.
Can Measure Minimum And Maximum Values Quicker
Similarly, If you need to see minimum and maximum values on a circuit, the needle helps you do so very quickly.
No Dependency On Power
Analog multimeters do not require batteries or a power supply. This ultimately keeps the cost of ownership lower and is more convenient if you are going to be using the multimeter for an extended period of time.
Cost
Analog multimeters are typically cheaper. Why pay more, if you don’t need extremely accurate measurements?
Complexity
Analog multimeters are almost the tool that won’t die. With its far simpler construction than digital multimeters, you can almost guarantee they will last a long time.
The Cons Of Using An Analog Multimeter
While we listed the relative benefits of digital multimeters above, there are some important disadvantages of analog multimeters needed to be discussed as well. The most obvious cons of using an analog multimeter are:
- Less Features
- Fragile
- Easy to Misread
- Extra Math Required
Less Features
Most importantly, they simply lack the extra features that most digital multimeters. Nearly everything in the world is moving to a digital format, for obvious reasons. The ability to add additional features into a digital multimeter is a huge benefit and not having that on an analog multimeter hinders its overall usability.
Fragile
Analog multimeters are slightly more fragile, given they display the readings on a fine needle. If the needle were to break, the multimeter becomes essentially unusable.
Easy To Misread
Analog multimeters are easy to misread, both from parallax error and using the wrong scale.
Extra Math Required
Oftentimes, you will have to do a lot of extra math in your head. Most digital multimeters will complete conversions and calculations directly in the unit itself. Analog multimeters lack this possibility due to not having an onboard microprocessor.
Conclusion
Today, digital multimeters lead with precision, smart features, and versatility for modern applications like EV maintenance and IoT design. Analog multimeters, though less common, excel in niche tasks like vintage repairs and education, offering simplicity and battery-free operation. Choose based on your project’s needs—DMMs for high-tech precision, analog for classic reliability. Ready to pick your tool? Explore top models or learn how to use them safely.
Analog Vs. Digital Multimeters FAQs
Q1. Are analog multimeters still used today?
Yes, analog multimeters are often used for vintage repairs, education, and battery-free operations.
Q2. Why are digital multimeters more accurate?
Digital multimeters offer digital processing and numerical displays to reduce errors and achieves ±0.1% vs. ±2% for analog.
Q3. Can analog multimeters measure fluctuating signals better?
Yes, needle movements on a analog multimeter shows real-time changes, unlike digital multimeter averages.
Q4. Are digital multimeters worth the higher cost?
For professional and complex tasks, yes, digital multimeters are worth the higher costs due to advanced features and precision.
The Definitive Guide To Multimeters
What’s Next: What Is The Difference Between A Handheld And Benchtop Multimeter?
Now that we know the relative pros and cons of the most common distinction of multimeters, analog vs. digital, there is one more very common distinction that needs to be discussed: portable vs. benchtop multimeters.
In the next section, we will dive into the different constructions of multimeters, portable vs. benchtop. Let’s get started and head to Section 7: Handheld vs. Benchtop Multimeters.
ISO/IEC 17025 Accredited Multimeter Calibration
Fox Valley Metrology offers precise multimeter calibration for any make or model. Our ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation guarantees testing to the highest industry standards. We offer fast, reliable in-lab or onsite calibration services to fit your needs and schedule.
- ✓ ISO/IEC 17025 accredited calibration vendor
- ✓ Broadest calibration scope in the industry
- ✓ 3-5 day turnaround time in-lab calibrations
- ✓ Pickup and delivery service options
- ✓ Onsite calibration available